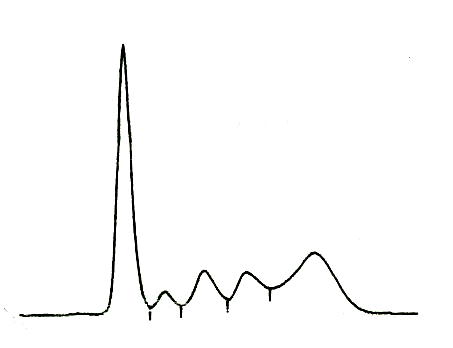
AIDS
|
TP |
Alb |
alpha-1 |
alpha-2 |
beta |
gamma |
|
7.70 |
3.42 |
0.32 |
0.83 |
0.92 |
2.31 (g/dL) |
CASE; 40-year-old Japanese male
COMMENTS:
This is the electrophoretic pattern of serum of a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) complicated by Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. While the increased gamma globulin fraction must be caused by AIDS itself, the increased alpha-2 globulin is considered to be due to the acute P. carinii pneumonia.
Hypergammaglobulinemia is the common and characteristic feature of AIDS. Florid histologic and/or functional aberrations and damages may occur in immune system of HIV infected individual. The various pathologic processes may play roles in the development of B-cell acitivation resulting in hypergammaglobulinemia of AIDS.
However, the clear explanation about the mechanisms of this dysproteinemia is not yet established.
1. Herndier
BG, McGrath ms. Pathogenesis of AIDS lymphomas. AIDS.. 1994;8:1025-49.
2. Yap PL, Williams PE. Immunoglobulin
preparations for HIV-infected patients. Vox Sang.
1988;55:65-74.
3. De Milito
A. B lymphocyte dysfunctions in HIV infection. Curr HIV Res.
2004;2:11-21.
4.Lane HC, Fauci AS. Immunologic abnormalities in the acquired
immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Rev Immunol. 1985;3:477-500.
2007/01/19 Takatoshi INOUE