s
Minimal Change Nephrosis
CASE: 25 -year-old male
HISTOPATHOLOGY: Minimal change nephrosis (MCN)
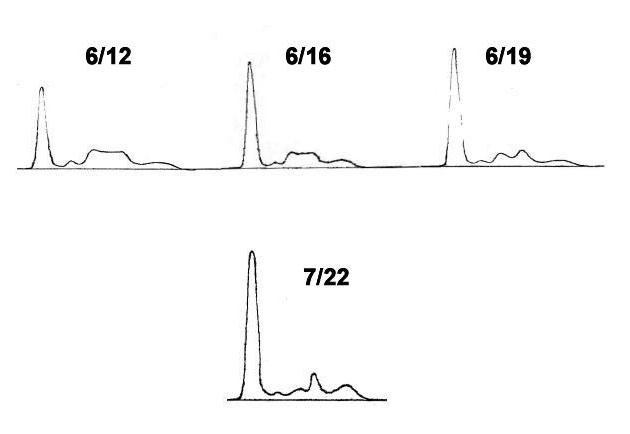
Figure 1-4. These patterns are modified as they represent absolute protein concentrations which are calculated by albumin levels.
Table 1. (g/dL)
|
Date |
TP |
Alb |
alpha-1 |
alpha-2 |
beta |
gamma |
|
6/12 |
3.6 |
1.7 |
0.16 |
0.75 |
0.73 |
0.30 |
|
6/16 |
4.7 |
2.8 |
0.15 |
0.60 |
0.71 |
0.43 |
|
6/19 |
5.1 |
3.4 |
0.16 |
0.53 |
0.74 |
0.33 |
|
7/22 |
6.8 |
4.5 |
0.21 |
0.49 |
0.81 |
0.90 |
Table 2. Other data at Jun 12 (mg/dL)
|
α1 AT |
Hp |
alpha-2M |
Tf |
C3 |
IgA |
IgM |
IgG |
|
134 |
104 |
395 |
138 |
80 |
182 |
106 |
510 |
On admission, daily about 4g of albuminuria persisted. The electrophoresis of serum protein showed a neprhrotic pattern characterized by elevated alpha-2 and beta globulin fractions. A marked decrease in gamma globulin fraction was also found (Figure and Table 1 and 2). The treatment with oral prednisolone of 40 mg daily was begun without intravenous supplementary albumin infusion.
COMMENTS
1. Albumin fraction:
His proteinuria became negative soon after the start of the therapy, and the serum albumin level was rapidly getting recovered.
Healthy adult individuals generally have approximate 100g of albumin in their whole serum. Its daily turn over is 10g, or the serum half life is 17 days. It is well known that, albumin synthesis is commonly accelerated in patients with nephrosis. When albumin leakage to urine reaches up to 4g per day or over, the serum albumin level must be getting decreased, and finally, when the serum albumin decreases to a level of just about 2.8g/dL or less, the patient falls into nephrotic state.
The patient's serum albumin level recovered 41.6g/dL (14%) per week at the initiation of the treatment. This was equivalent to a daily 6 percent (41.6/7 = 6%) recovery, or to a daily 6g increase in the serum albumin. This suggests that, according to circumstances, an acceleration of albumin synthesis can be lifted up to a level of approximate 6g per day.
2. Alpha-2 fraction:
One week after the start of oral steroid therapy , the serum alpha-2 globulin fraction was found to be markedly decreased (Figure 6/19).
In patients with nephrosis, alpha-2 macroglobulin (alpha-2M) is chiefly responsible for an increase in electrophoretic alpha-2 globulin fraction. The molecular weight of alpha-2M is as large as 760kDa, which is too large to penetrate glomerular capillary walls. Then the serum concentration of alpha-2M not depends on its loss to urine, but only on the balance of its synthesis and the turn over rate.
The sharp response to corticosteroid found in alpha-2 globulin fraction of this patient agrees with the recent concepts that the serum half life of alpha-2M is as short as 4 or 5 days, and its accelerated synthesis is the only cause of its increased absolute amount in nephrosis.
3. Gamma globulin fraction:
In this patient, markedly decreased serum levels of gamma globulin/IgG would not be recovered by the treatment.
Even in a milder glomerular injury like as MCN, an alteration in glomerular electric negative charge (charge-selectivity) may occur which results in albumin leakage to urine, meanwhile, the serum immunoglobulins hardly penetrate glomerular capillary walls because of their electric charge. However , in some kind of severe glomerular diseases, a morphological damage in glomerular capillary may occur, which results in leakage of many kinds of serum proteins to urine regardless of their electric charge and/or of their molecular size. The loss of gamma globulin to urine, which can be detectable as hypogammaglobulinemia in nephrosis, represents the presence not only of the failure in charge-selectivity, but also in seize-selectivity.
In spite of this patient's histopathology was diagnosed as a mild glomerular disease of MCN, in which seize selectivity is usually normal while only charge selectivity failure is common, the serum gamma globulin/IgG concentrations were decreased and persisted until he got a complete remission later. The delayed recovery in serum gamma globulin levels can be explained by the lack of acceleration of immunoglobulin synthesis in nephrosis. However, the cause of the decrease in serum gamma globulin concentrations in this patient can not be understand by generally accepted concepts of the glomerular protein selectivity as described above.
4. Alpha-1 globulin and beta globulin fractions:
The main elements of alpha-1 globulin and beta globulin are alpha-1 antitrypsin (alpha-1 AT; MW 51 kDa) and transferrin (Tf; MW 80 kDa), respectively, and their serum half lives are about 7 days in both proteins.
Both charge- and seize-selectivity failures must contribute to their leakage to urine. The normal concentrations found in both two proteins at the nephrotic condition must be held by the accelerated synthesis of each protein.
REFERENCES
1. de Sain-van der Velden MG, et al. Plasma alpha 2
macroglobulin is increased in nephrotic patients as a result of increased
synthesis alone. Kidney Int 1998;54:530-5.
2.
Tencer J, et al. Proteinuria selectivity index based upon alpha-2-macroglobulin
or IgM is superior to the IgG based index in differentiating glomerular
diseases. Technical note. Kidney Int 1998;54:2098-105.
Feb 07 Takatoshi INOUE, M.D.